Healthcare Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology is rapidly evolving and aims to utilize theLarge Language Models(LLMs) has enormous potential to revolutionize the way healthcare is delivered. These technological advances promise to improve diagnostic accuracy, personalize treatment plans, and unlock access to comprehensive medical knowledge, fundamentally transforming patient care. Integrating AI into healthcare aims to improve the efficiency and accuracy of healthcare delivery, effectively bridging the gap between the technological frontier and patient-centered care.
Linguistic diversity in global healthcare delivery is a major challenge. While medical knowledge is dominated by English, the effectiveness of healthcare delivery in non-English-speaking regions relies heavily on the availability of medical information in local languages. This situation highlights the urgent need to make healthcare AI technologies universally accessible, thereby extending their benefits to a global audience that includes more than 6 billion people who speak a variety of languages.
Researchers from the Shenzhen Big Data Research Institute and the Shenzhen Research Institute of the Chinese University of Hong Kong have launched the Apollo, a groundbreaking suite of multilingual medical LLMs that marks a significant advance in the inclusivity of medical AI.
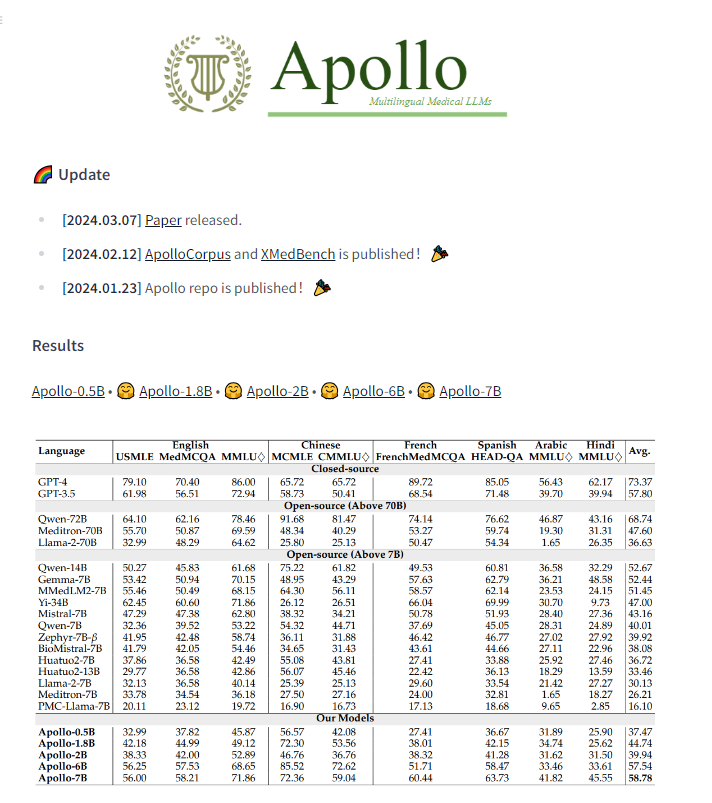
Apollo models are carefully trained using ApolloCorpora, a large multilingual dataset, and rigorously evaluated against the XMedBench benchmark. This strategic approach enables Apollo to match or exceed the performance of existing models of equivalent size across a range of languages, including English, Chinese, French, Spanish, Arabic, and Hindi, demonstrating its unrivaled versatility.
The methodology behind Apollo development focuses on rewriting a pre-trained corpus into a question and answer format and using adaptive sampling of the training data. This approach makes learning transitions seamless, resulting in the training of smaller but efficient models. These models not only excel at understanding and generating multilingual medical information, but also augment larger models with a novel agent tuning technique that eliminates the need for direct fine-tuning.
Apollo's models, particularly Apollo-7B, have performed exceptionally well, setting a new standard for multilingual medical LLMs. This achievement demonstrates Apollo's potential to democratize medical AI, enablingCutting EdgeMedical knowledge is universally accessible across language barriers. In addition, Apollo significantly enhances the multilingual medical capabilities of larger general-purpose LLMs, illustrating its critical role in the global rollout of medical AI technology.
The Apollo project has become a progressive light in the democratization of medical AI, aiming to make complex medical knowledge universally accessible, regardless of language barriers. The initiative bridges an important gap in global medical communication and lays the foundation for future multilingual medical AI innovations.
Paper URL:https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.03640