Today we will continue to explore the advanced techniques of localized repainting, including the mask mode, mask area content processing, knowledge about repainting area, and some notes on localized repainting. We will use AI model face change as a real-world case to help you deeply understand and master the essence of local repainting.
I. Masking mode
Mask mode is a technique we often use in local repainting, which is divided into two modes: repainting masked content and repainting non-masked content, which corresponds to different demand scenarios.
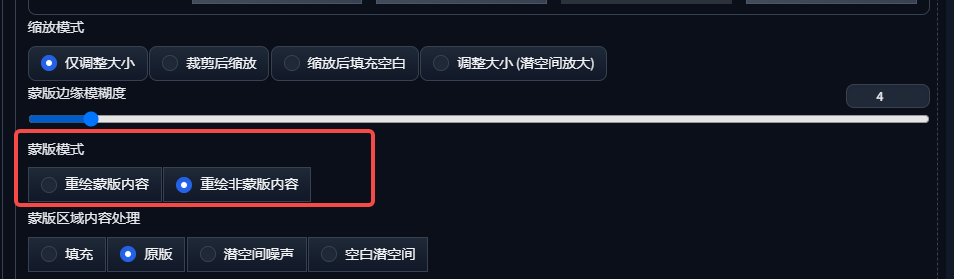
1. Redraw the content of the mask
Ideal for when you need to change a specific area such as a model's background or clothes while keeping the rest of the model unchanged.
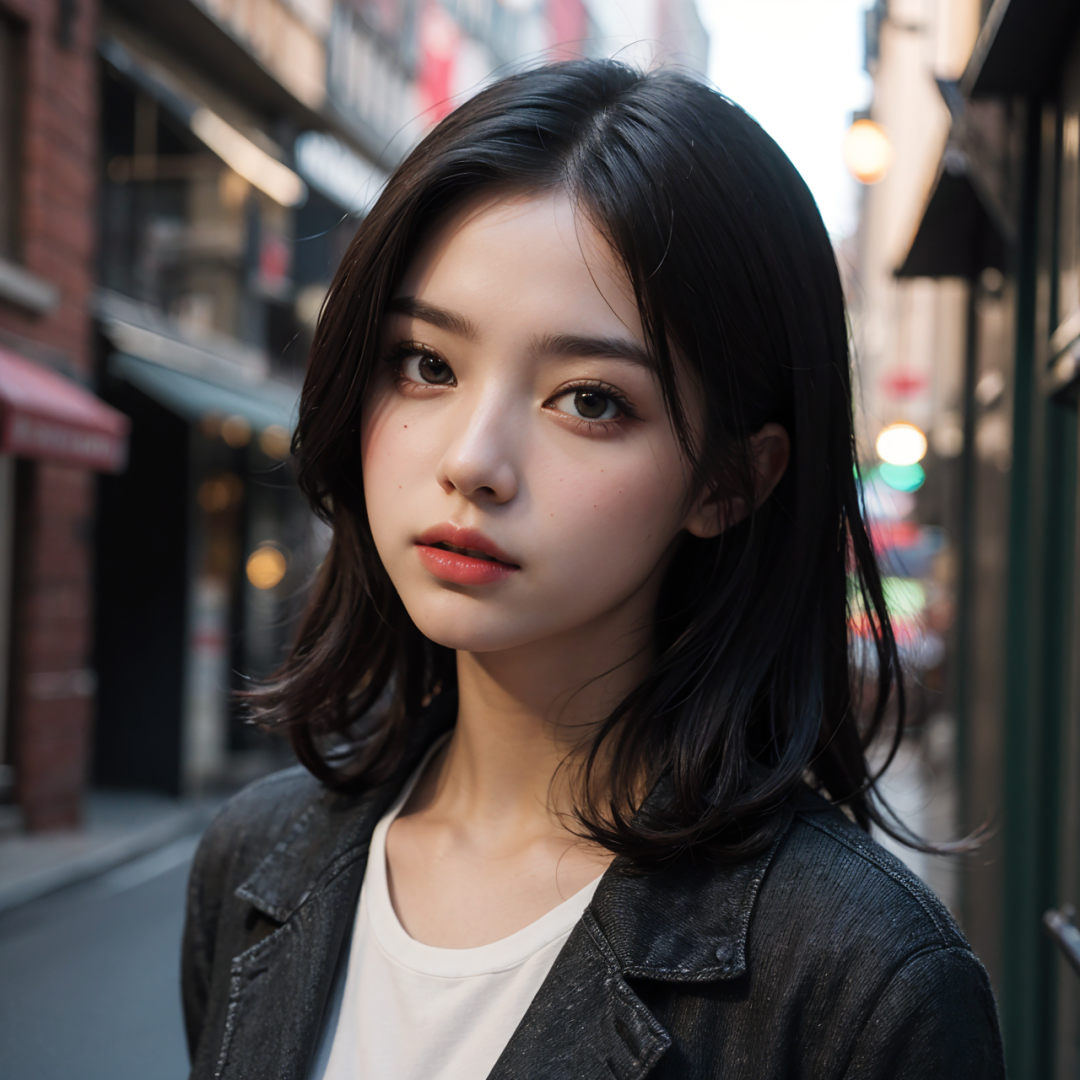
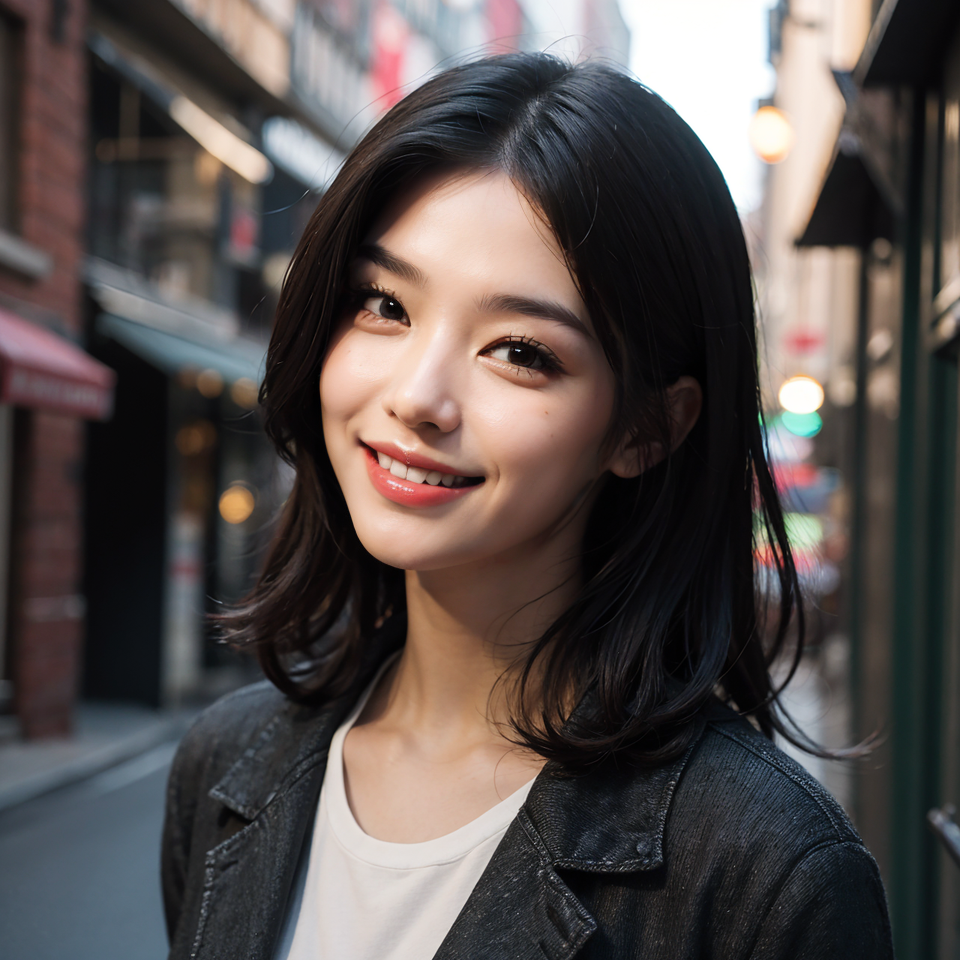


2. Redraw non-masked content
Ideal for all areas where the face needs to be preserved and all areas outside the face need to be altered.
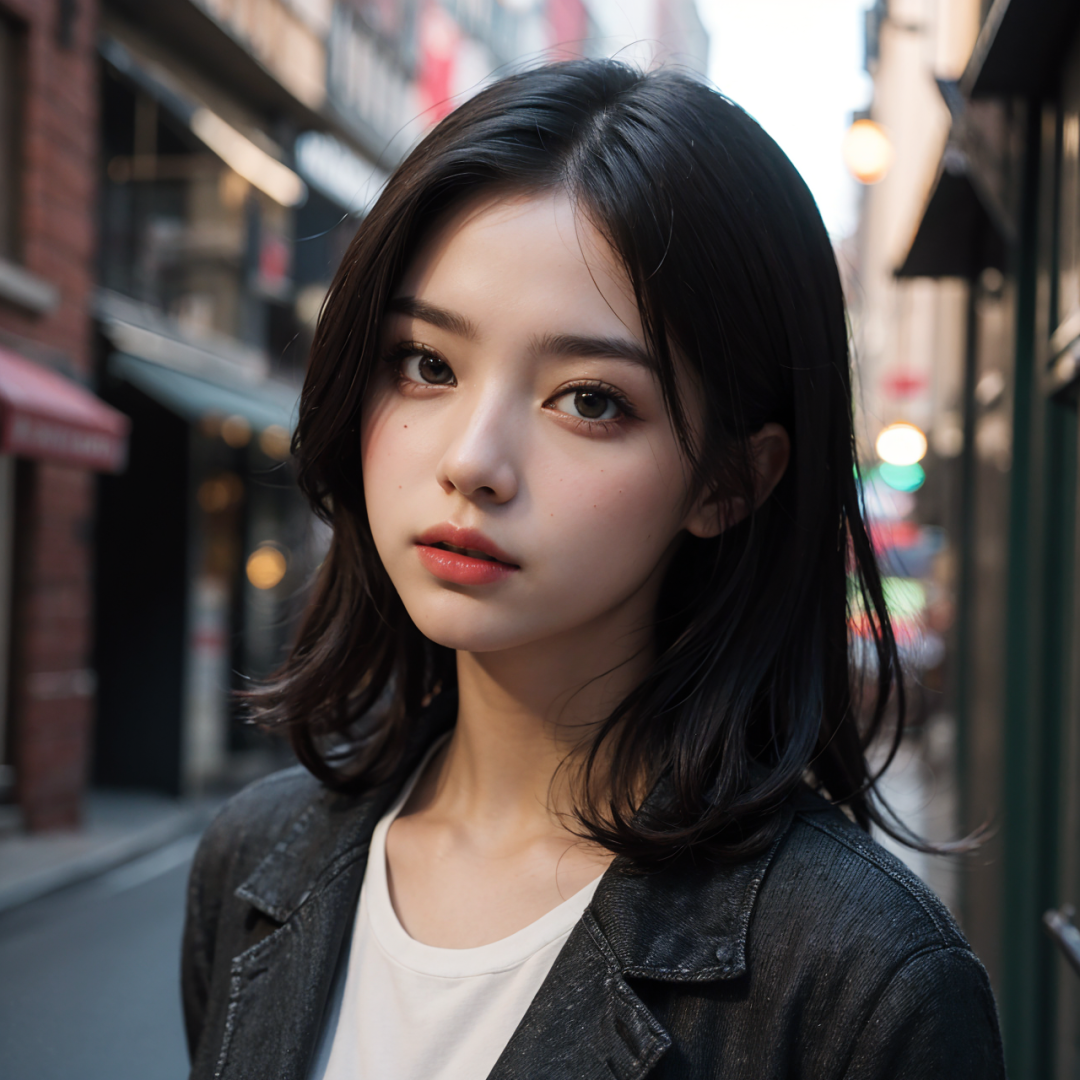
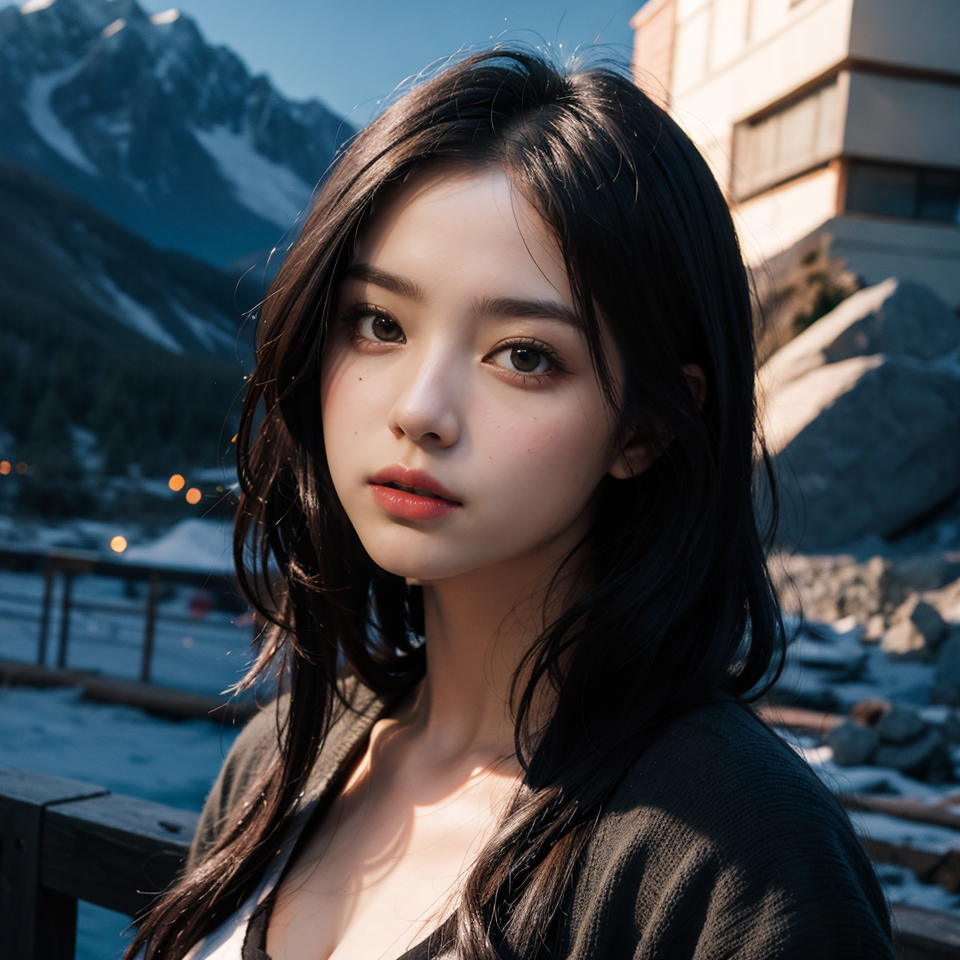


By adjusting the mask mode, we can precisely control which areas need to be redrawn to achieve the desired effect.
Second, the mask area content processing
Masked area content handling is the most difficult part of localized repainting to master, but it is also the most critical. It involves how to completely erase the original image information and fill in new content where the mask has been applied.
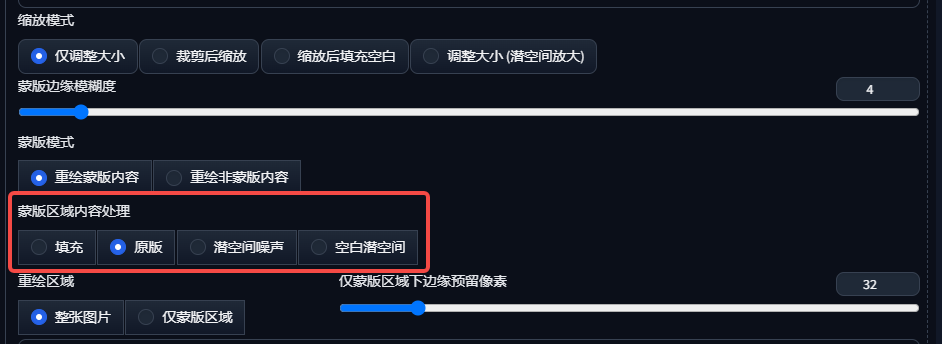
1. Filling mode
Fill the mask area with the blurred pixels of the original image, slightly refer to the tone of the original image for repainting, the repainting amplitude should be greater than 0.8.

2. Original Mode
The most commonly used mode, based on the original image on the basis of laying noise and then denoising, redrawing the magnitude of the small time with the original image correlation is high, large time is irrelevant, redrawing the magnitude of the magnitude of 0-1 can be between.

3. Latent space noise
Filled with noise to completely erase the information of the original image, the redrawing effect is so thorough that the redrawing amplitude should be greater than 0.8.

4. Gap latent space
After erasing all the original information, fill in a uniform brown color to achieve a consistent redraw of the base map color, and the redraw margin should be greater than 0.8.

Third, redraw area: the whole picture and only the mask area
The setting of the redraw area determines theStable DiffusionThe range of pixels calculated, divided into two options: whole image and masked area only.
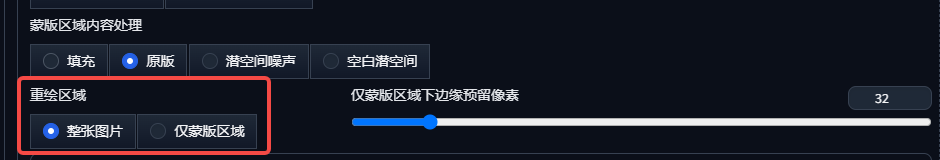
1. Whole picture
Considering the content of the whole map to generate the localization, the accuracy of the generation is high, but it is impossible to redraw the oversized map or the high precision redrawing of the small size map.

2. Masked area only
Considering only the redrawn part to generate localized content, independent of resolution, it is suitable for high-precision redrawing of oversized and small-sized drawings.

2.1 Reserve pixels for the lower edge of the mask area only
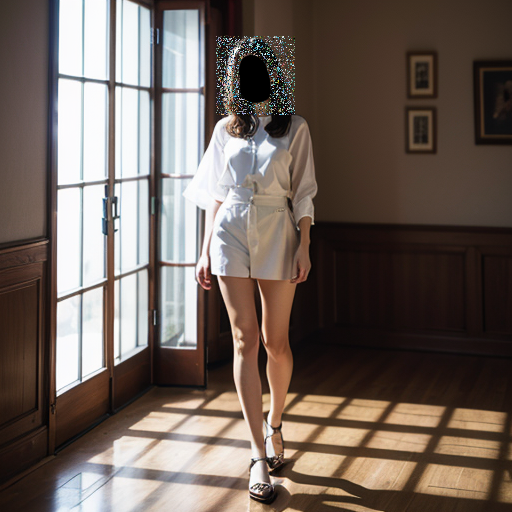

2.2 Effect of edge reserved pixel parameters on facial pixel density
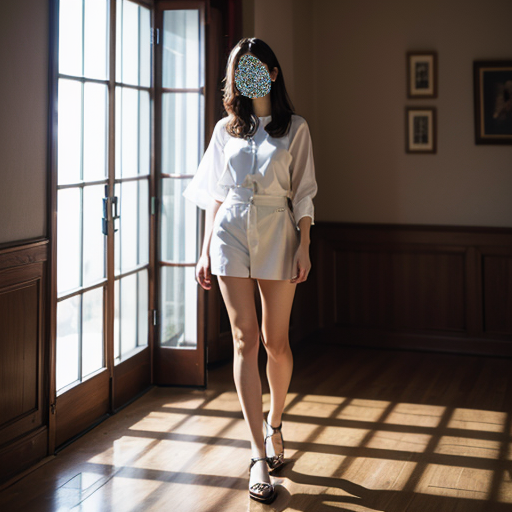

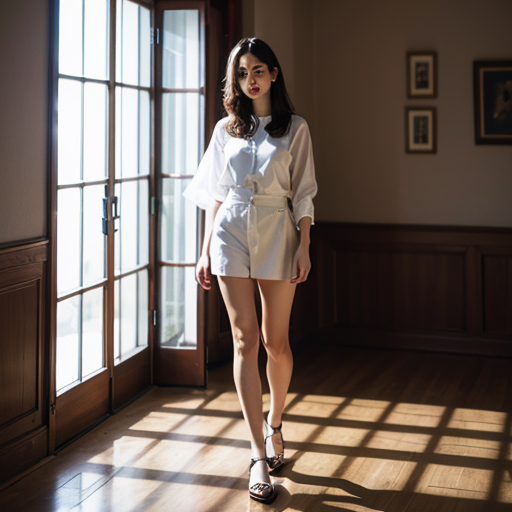
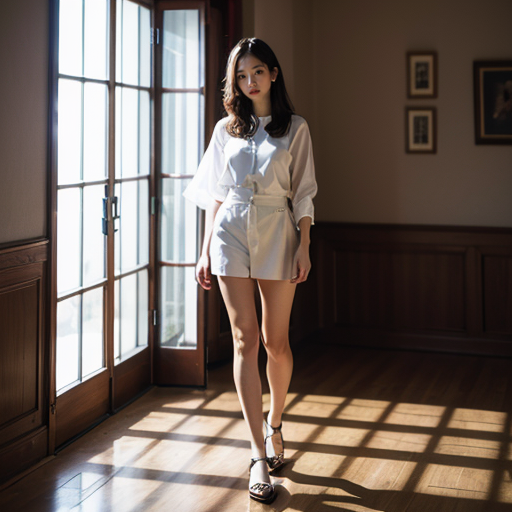
IV. Application Case: AI Model Face Change
We will demonstrate how to apply the theoretical knowledge of localized repainting to real projects through the case of AI model face swap.
By adjusting the mask mode and repainting areas, we can accurately replace the model's face with Lora while keeping the rest of the area consistent.
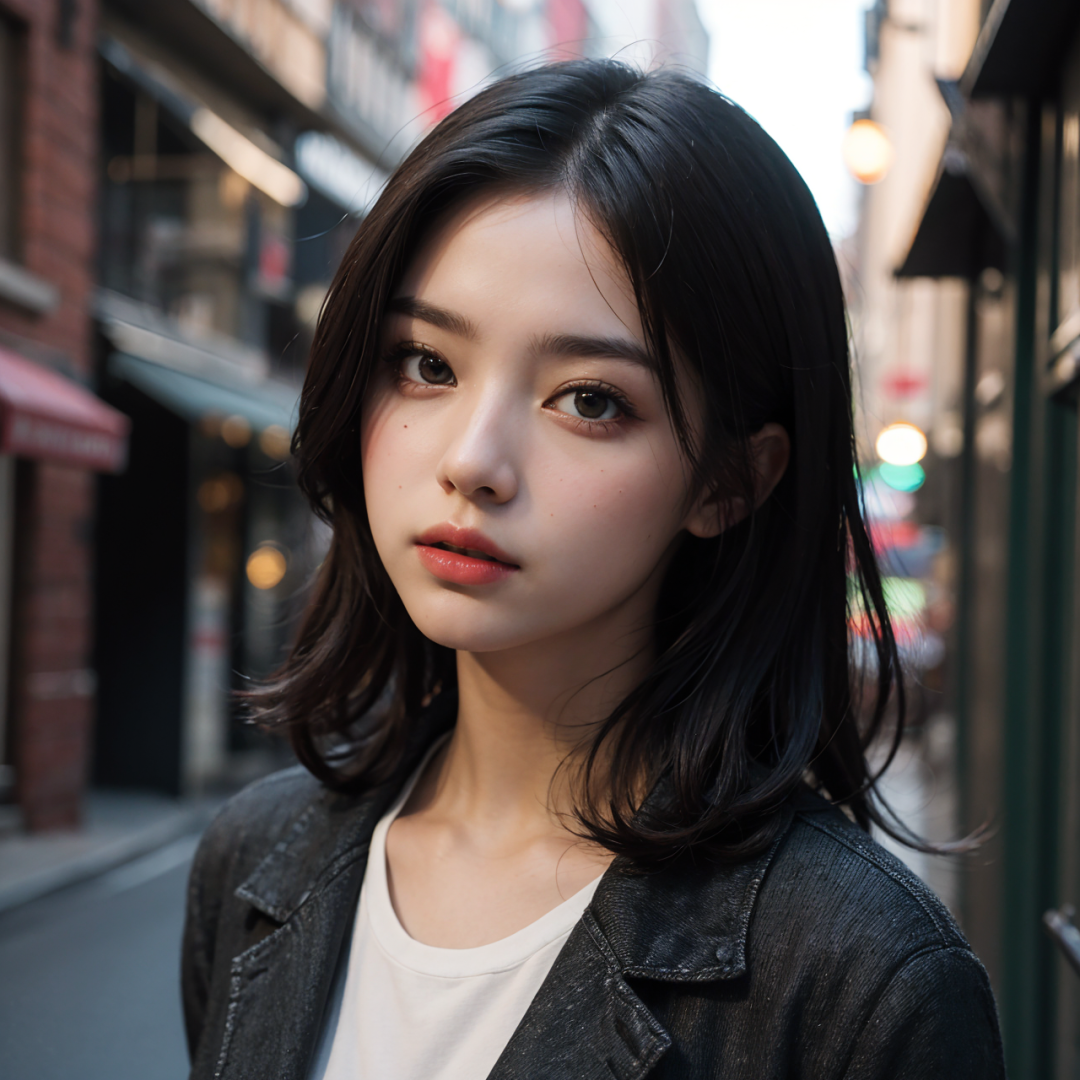
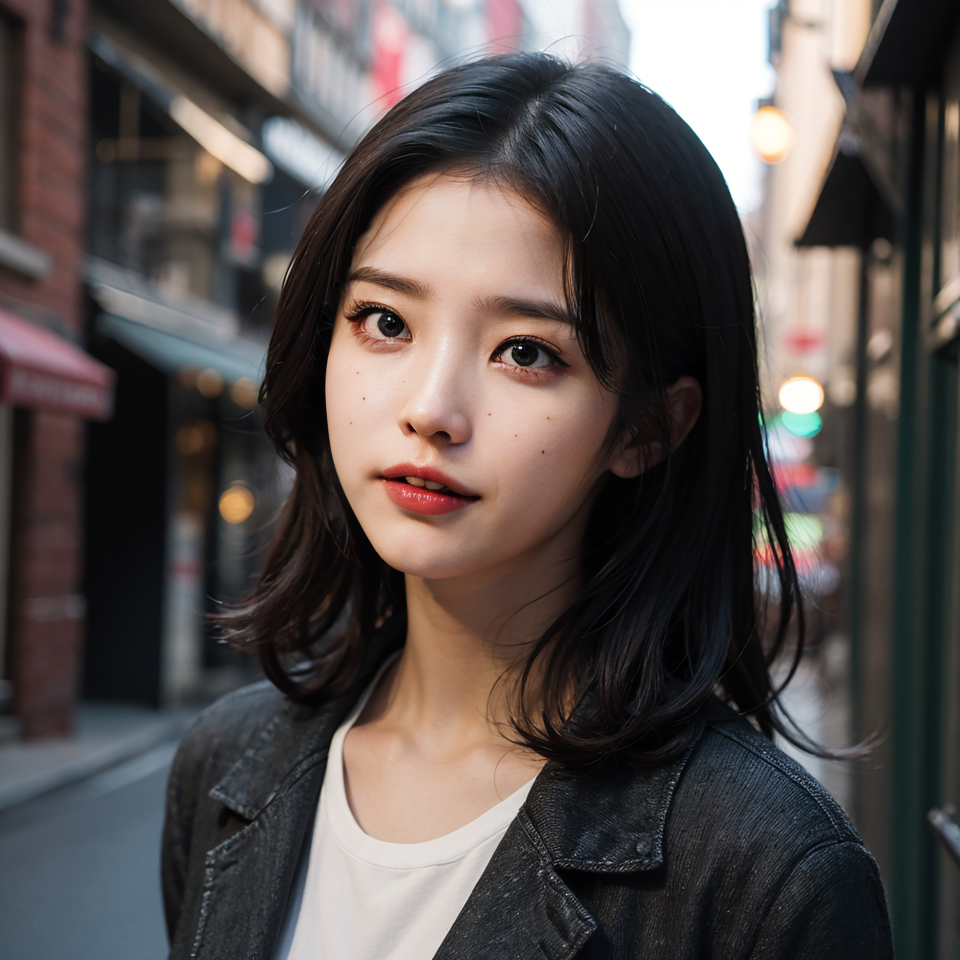


V. Summary
In this section, we have learned the advanced knowledge of Stable Diffusion local repainting, these knowledge is difficult, but through repeated practice and practice, I believe you will be able to integrate these knowledge points. In future projects, these skills will shine.
I hope this article can help you deeply understand Stable Diffusion's local redraw feature and flexibly use it in real projects.