
The rate of progress in the field of AI is truly moving at an unprecedented pace. In just over a week, theDeepSeek-R1 LLM models have rocked the AI world with the release of their impressive accuracy, which is comparable to existing models but created at a fraction of the typical cost.
The DeepSeek team has managed to distill the inference power of its massive 671B parametric model into 6 smaller models based on Qwen (DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B, 7B, 14B and 32B) and Llama (DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-8B and 70B). This effectively means that you can use your own copy of the model - customize it, make changes, run it locally or host it on a cloud platform.
In this paper, we use Python Building a DeepSeek-R1 ChatbotsIn short, Streamlit is used on the front end. In short, Streamlit is used on the front-end, while on the back-end, API calls to the DeepSeek-R1 model hosted in Snowflake enable the implementation of LLM models that provide support for application responses.
Clickhere areCheck out the GitHub repository for this tutorial.
1、What is DeepSeek-R1?
In short, DeepSeek-R1 is an inference model that uses reinforcement learning to teach the basic language model DeepSeek-V3 to reason without human supervision.
Here are the 5 main features of DeepSeek-R1:
- State-of-the-art reasoning: DeepSeek-R1 can achieve an accuracy of 97.3% on advanced math tasks, outperforming earlier benchmarks. Similarly, its score of 79.8% on AIME 2024 and 49.2% on SWE-bench Verified outperforms other models.
- Cost efficiency: DeepSeek models are significantly cheaper to train than industry standards
- Wide range of applications: excels in creative writing, long contextual comprehension and factual quizzes.
- Scalability: The model is available in several compact versions (1.5B to 70B parameters), which optimizes the balance between capacity and resource use.
- Accessibility: Open source availability allows developers and researchers to try out the model to apply advanced AI tools to real projects.
Despite its excellent performance, there may still be concerns about the security aspects of its use. With this in mind, since the model is open source, the underlying code can be inspected and the model itself can be self-deployed on the user's own computing resources.
In this tutorial, we'll use a tutorial hosted on the DeepSeek-R1 model in the Snowflake platform.
2. Overview of the application
Here is a high-level overview of the DeepSeek-R1 chatbot app:
- The user provides prompted input (i.e., asks questions).
- An LLM call is made using SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX.COMPLETE(), which submits the prompted input and gets the LLM-generated response and displays it in the application.
3. Operation of chatbots
Let's see the chatbot in action by launching the chatbot and typing a question into the chat input:

As a reasoning model, LLM first enters the thinking phase:

Once the thought process is complete, the final answer will be shown below:
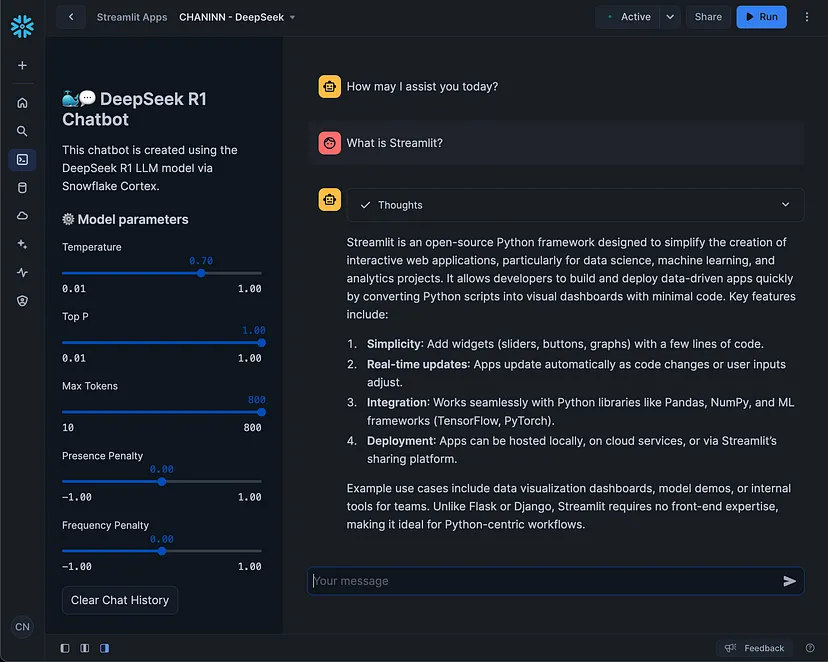
It should be noted that the depth of thinking and answers is directly affected by the maximum token parameter. Here, we have limited the maximum tokens to 800 for testing purposes, but you can increase this to 20,480.
4. Building the DeepSeek-R1 chatbot
Now let's move on to building the DeepSeek-R1 chatbot on the Snowflake platform.
4.1 Setting up the development environment
To access the necessary tools, make sure you have access to a Snowflake account.
Next, navigate to Streamlit in Snowflake, go to Project → Streamlit, and click + Streamlit App to create the app (you will then specify the app location and repository):

Next, you'll see a sample starter app to help get started:

The Streamlit interface in Snowflake is similar to an online code editor, where you can edit code on the left and view the rendered application on the right.
Go ahead and replace it with the application we're building today.
4.2 Retrieving codes
The DeepSeek-R1 chatbot application we're building today consists of the following components:
- environment.yml - environment dependencies for the application
- streamlit_app.py - Streamlit application file
First, the contents of the environment.yml file are shown below:
name: app_environmentchannels: snowflake- snowflakedependencies: Python=3.11.*- snowflake-ml-Python- snowflake-ml-Python- snowflake-snowpark-Python- streamlit
Next, the contents of the sis_app.py file are shown below:
import streamlit as stfrom snowflake.snowpark.context import get_active_sessionimport pandas as pdimport jsonimport re# App configurationst.set_page_config(page_title="🐳💬 DeepSeek R1 Chatbot", initial_sidebar_state="expanded")session = get_active_session()# Helper functionsdef clear_chat_history(): st.session_state.st.session_state.messages = [{"role": "assistant", "content": "How may I assist you today?"}]def escape_sql_string(s):: return s.replace("'").return s.replace("'", "''")def extract_think_content(response).think_pattern = r'(. *?) 'think_match = re.search(think_pattern, response, re.DOTALL)if think_match.think_content = think_match.group(1).strip()main_response = re.sub(think_pattern, '', response, flags=re.DOTALL).strip()return think_content, main_responsereturn None, responsedef generate_deepseek_response(prompt, **params):string_dialogue = "".join(f"{msg['content']}\n\n"for msg in st.session_state.messages)cortex_prompt = f"'[INST] {string_dialogue}{prompt} [/INST]'"prompt_data = [{'role': 'user', 'content': cortex_prompt}], paramsprompt_json = escape_sql_string(json.dumps(prompt_data))response = session.sql("select snowflake.cortex.complete(? , ?)" ,params=['deepseek-r1', prompt_json]).collect()[0][0]return response# Model parameters configurationMODEL_PARAMS = {'top_p': {'min': 0.01, 'max': 1.0, 'default': 1.0, 'step': 0.01},'presence_penalty': {'min': -1.0, 'max': 1.0, 'default': 0.0, 'step': 0.1},'frequency_penalty': {'min': -1.0, 'max': 1.0, 'default': 0.0, 'step': 0.1}}# Sidebar UIwith st.sidebar.st.title('🐳💬 DeepSeek R1 Chatbot')st.write('This chatbot is created using the DeepSeek R1 LLM model via Snowflake Cortex.')st.subheader('⚙️ Model parameters')params = {param: st.sidebar.slider(param.replace('_', ' ').title(),min_value=settings['min'],max_value=settings['max'],value=settings['default'],step=settings['step'])for param, settings in MODEL_PARAMS.items()}st.button('Clear Chat History', on_click=clear_chat_history)# Initialize chat historyif "messages" not in st.session_state: st.session_state.st.session_state.messages = [{"role": "assistant", "content": "How may I assist you today?"}]# Display chat messagesfor message in st.session_state.messages: with st.chat_message.with st.chat_message(message["role"]):st.write(message["content"])# Handle user inputif prompt := st.chat_input(): with st.chat_message(message["role"]: st.write(message["content"])with st.chat_message("user").st.write(prompt)st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "user", "content": prompt})if st.session_state.messages[-1]["role"] ! = "assistant": if st.session_state.messages[-1]["role"] !with st.chat_message("assistant")::status_container = st.status("Thinking ..." , expanded=True)with status_container: response = generate_deepseekresponse = generate_deepseek_response(prompt, **params)think_content, main_response = extract_think_content(response)if think_content.st.write(think_content)status_container.update(label="Thoughts", state="complete", expanded=False)st.markdown(main_response)st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": main_response})
You can also get the DeepSeek-R1 chatbot from here. Github RepositoriesDownload the necessary application files.
4.3 Running the application
To run the application, copy and paste the above code and click the Run button.

You can place the mouse cursor on the divider of the Code/Application panel and move it to the left until the Code panel disappears (see below). This will expand the application panel to full screen.
Continue and type in the prompt to start your chat session:

Also, see the Chatbot Hands-On section above for the thought process and answers generated by LLM.
5. Code description
Let's explore what each code block is doing ......
5.1 Importing libraries
We'll start by importing the prerequisite library.
import streamlit as stfrom snowflake.snowpark.context import get_active_sessionimport pandas as pdimport jsonimport re
5.2 Application configuration
Next, we use st.set_page_config() to define the application pages and set their initial page parameters, and we'll set initial_sidebar_state="expanded" so that they do exactly that, expanding the sidebar. Here we also set the session variable, which we'll use later.
# App configurationst.set_page_config(page_title="🐳💬 DeepSeek R1 Chatbot", initial_sidebar_state="expanded")session = get_active_session()
5.3 Auxiliary Functions
In this section, we define several helper functions that will be used in later parts of the application:
- clear_chat_history() - this allows us to clear the chat history to its initial state
- escape_sql_string() - replaces the SQL string when performing some text formatting
- extract_think_content() - parses and separates the content contained in the XML style "think" tags ( and ) and separates it from the final response.
# Helper functionsdef clear_chat_history(): st.session_state.messages = [{"role": "assistant"?st.session_state.messages = [{"role": "assistant", "content": "How may I assist you today?"}]def escape_sql_string(s):: return s.replace("'").return s.replace("'", "''")def extract_think_content(response).think_pattern = r'(. *?) 'think_match = re.search(think_pattern, response, re.DOTALL)if think_match.think_content = think_match.group(1).strip()main_response = re.sub(think_pattern, '', response, flags=re.DOTALL).strip()return think_content, main_responsereturn None, response
For example, suppose we have the following generated response:
Let me analyze this problem step by step... </Here's the solution you're looking for...Here's the solution you're looking for...
It will parse and separate as:
- think_content: "Let me analyze this step by step ......"
- main_response: "This is the solution you are looking for ......"
Let's move on to the last helper function:
- generate_deepseek_response() - generates an LLM response using Snowflake's Cortex service and the DeepSeek R1 model
def generate_deepseek_response(prompt, **params):string_dialogue= "".join(f"{msg['content']}\n\n"for msg in st.session_state.messages)cortex_prompt = f"'[INST] {string_dialogue}{prompt} [/INST]'"prompt_data = [{'role': 'user', 'content': cortex_prompt}], paramsprompt_json = escape_sql_string(json.dumps(prompt_data))response = session.sql("select snowflake.cortex.complete(? , ?)" ,params=['deepseek-r1', prompt_json]).collect()[0][0]return response
5.4 Sidebar UI
We start by defining the variables in a dictionary format containing the model parameters and the associated minimum, maximum, default and step values.
MODEL_PARAMS
Next, we'll define the sidebar that starts with the application title and application description. Here we also include several slider widgets created by iterating through a for loop. Finally, we have a clear chat history button that calls the clear_chat_history callback function to reset the history to its initial state.
# Model parameters configurationMODEL_PARAMS= {'temperature': {'min': 0.01, 'max': 1.0, 'default': 0.7, 'step': 0.01}, 'top_p': {'min': 0.01, 'max': 1.0, 'default': 1.0, 'step': 1.0'top_p': {'min': 0.01, 'max': 1.0, 'default': 1.0, 'step': 0.01},'presence_penalty': {'min': -1.0, 'max': 1.0, 'default': 0.0, 'step': 0.1},'frequency_penalty': {'min': -1.0, 'max': 1.0, 'default': 0.0, 'step': 0.1}}# Sidebar UIwith st.sidebar.st.title('🐳💬 DeepSeek R1 Chatbot')st.write('This chatbot is created using the DeepSeek R1 LLM model via Snowflake Cortex.')st.subheader('⚙️ Model parameters')params = {param: st.sidebar.slider(param.replace('_', ' ').title(),min_value=settings['min'],max_value=settings['max'],value=settings['default'],step=settings['step'])for param, settings in MODEL_PARAMS.items()}st.button('Clear Chat History', on_click=clear_chat_history)
5.5 Chat Elements
In the final part of the application, we will initialize the session state variables of the chat history, iteratively display incoming chat messages, and finally define the conditional flow that handles the user/application chat logic. The latter section utilizes previously defined helper functions to process LLM-generated responses.
# Initialize chat historyif "messages" not in st.session_state: [{"role": "assistant": "content": "How may I assist you today?st.session_state.messages = [{"role": "assistant", "content": "How may I assist you today?"}]# Display chat messagesfor message in st.session_state.messages: with st.chat_message.with st.chat_message(message["role"]):st.write(message["content"])# Handle user inputif prompt := st.chat_input(): with st.chat_message(message["role"]: st.write(message["content"])with st.chat_message("user").st.write(prompt)st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "user", "content": prompt})if st.session_state.messages[-1]["role"] ! = "assistant": if st.session_state.messages[-1]["role"] !with st.chat_message("assistant")::status_container = st.status("Thinking ..." , expanded=True)with status_container: response = generate_deepseekresponse = generate_deepseek_response(prompt, **params)think_content, main_response = extract_think_content(response)if think_content.st.write(think_content)status_container.update(label="Thoughts", state="complete", expanded=False)st.markdown(main_response)st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": main_response})
Putting these code blocks together, we get the DeepSeek-R1 chatbot!
6. Concluding remarks
Build your own chatbot powered by the powerful DeepSeek-R1 model. This is impressively implemented in less than 100 lines of code.
You may notice that a large portion of the code involves the handling of "think" tags and a lot of inline comments, which, if removed, would make the application much smaller.